how many cells are formed as a result of mitosis|The cell cycle and mitosis review (article) : Clark Numerous descriptions of cell division were made during 18th and 19th centuries, with various degrees of accuracy. In 1835, the German botanist Hugo von Mohl, described cell division in the green algae Cladophora glomerata, stating that multiplication . Tingnan ang higit pa
Electronic Flow Meters - Code 5050 Parker Conflow’s Code 5050 is an electronic flowmeter that has a user-friendly display and is used for measuring and outputting flow rate, pressure and temperature. 1 Product Viewing 10 of 1 Show More . Close. F65/F150 The Porter Models F65 and F150 Forged Body Flowmeters feature a compact, one .
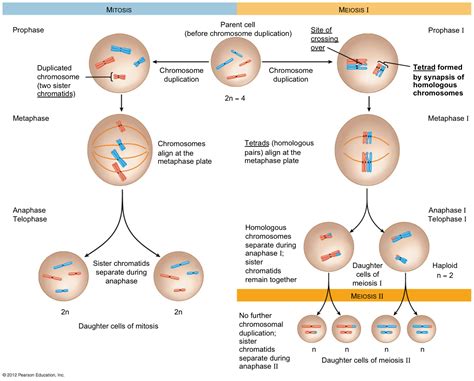
how many cells are formed as a result of mitosis,Overview The primary result of mitosis and cytokinesis is the transfer of a parent cell's genome into two daughter cells. The genome is composed of a number of chromosomes—complexes of tightly coiled DNA that contain genetic information vital for proper cell function. Because each resultant . Tingnan ang higit pa
Mitosis is a part of the cell cycle in which replicated chromosomes are separated into two new nuclei. Cell division by mitosis is an equational division which gives rise to genetically identical cells in which the total number . Tingnan ang higit pa
The cell cycle and mitosis review (article) The function or significance of mitosis, is the maintenance of the chromosomal set; each formed cell receives chromosomes that are. Tingnan ang higit paIn histopathology, the mitosis rate (mitotic count or mitotic index) is an important parameter in various types of tissue samples, for diagnosis as well as to further specify the. Tingnan ang higit pahow many cells are formed as a result of mitosisIn histopathology, the mitosis rate (mitotic count or mitotic index) is an important parameter in various types of tissue samples, for diagnosis as well as to further specify the. Tingnan ang higit paThere are prokaryotic homologs of all the key molecules of eukaryotic mitosis (e.g., actins, tubulins). Being a universal eukaryotic property, mitosis probably arose at the base of the eukaryotic tree. As mitosis is less complex than meiosis, meiosis . Tingnan ang higit pa

Numerous descriptions of cell division were made during 18th and 19th centuries, with various degrees of accuracy. In 1835, the German botanist Hugo von Mohl, described cell division in the green algae Cladophora glomerata, stating that multiplication . Tingnan ang higit paForms of mitosisThe mitosis process in the cells of eukaryotic organisms follows a similar pattern, but with variations in three main details.. Tingnan ang higit paCell roundingIn animal tissue, most cells round up to a near-spherical shape during mitosis. In epithelia and epidermis, an efficient rounding process is correlated with proper mitotic spindle alignment and subsequent correct . Tingnan ang higit pa
Mitosis is the division of a cell into two daughter cells that are genetically identical to the parent cell. Meiosis is the division of a .how many cells are formed as a result of mitosis The cell cycle and mitosis review (article) Generally speaking, the answer is straightforward: many cells come from just one by repeated cell division. Your first form as a zygote split to make two cells. Then those cells split, making four.and so on and so forth, .During mitosis, chromosomes become attached to the structure known as the mitotic spindle.In the late 1800s, Theodor Boveri created the earliest detailed drawings of the .
The purpose of mitosis is to produce more cells. After the first round of mitosis, there are only two cells. These cells both .

Mitosis consists of four basic phases: prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. Some textbooks list five, breaking prophase into an early phase (called prophase) and a late phase (called prometaphase). These .Mitosis is the process in which a eukaryotic cell nucleus splits in two, followed by division of the parent cell into two daughter cells. The word "mitosis" means "threads," and it refers to the .The cell cycle. In eukaryotic cells, the cell cycle is divided into two major phases: interphase and mitosis (or the mitotic (M) phase). Interphase is the longest part of the .
how many cells are formed as a result of mitosis|The cell cycle and mitosis review (article)
PH0 · mitosis / cell division
PH1 · The cell cycle and mitosis review (article)
PH2 · Phases of mitosis
PH3 · Mitosis (article)
PH4 · Mitosis
PH5 · Cell Division: Stages of Mitosis
PH6 · 25.1: Cell division: Mitosis